# 「力扣」第 230 题:二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素(中等)
- 题目链接:230. 二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素 (opens new window);
- 题解链接:递归与非递归写法(同理完成第 144、94、145 题,Python 代码、Java 代码) (opens new window)。
# 题目描述
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,请你设计一个算法查找其中第 k 个最小元素(从 1 开始计数)。
示例 1:
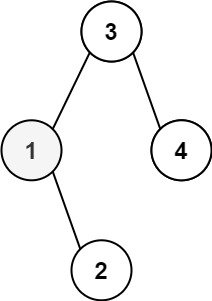
输入:root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1
输出:1
示例 2:
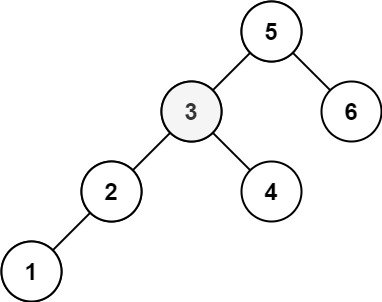
输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3
输出:3
提示:
- 树中的节点数为
n。 1 <= k <= n <= 10^40 <= Node.val <= 10^4
**进阶:**如果二叉搜索树经常被修改(插入/删除操作)并且你需要频繁地查找第 k 小的值,你将如何优化算法?
# 思路分析
利用“二叉搜索树”在“中序遍历”以后,得到的是有序数组,那么我们就中序遍历好了,遍历到第
我写下来发现递归的写法比较容易写错,要设置全局变量,而非递归的写法还相对比较“通用”且好理解。
参考代码 1:使用递归“中序遍历”。
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# 使用递归的方法,中序遍历
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.counter = 0
self.res = 0
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
# 递归执行左子树的逻辑
if root.left:
# 不是空,才继续遍历
self.kthSmallest(root.left, k)
# 在这里执行操作,数到第 k 个即可
self.counter += 1
# print(root.val)
if self.counter == k:
# 注意:千万不能在这里返回,后序遍历还要继续进行下去
self.res = root.val
# 注意:这里不能加 return
# 递归执行右子树的逻辑
if root.right:
self.kthSmallest(root.right, k)
return self.res
if __name__ == '__main__':
node3 = TreeNode(3)
node1 = TreeNode(1)
node4 = TreeNode(4)
node2 = TreeNode(2)
node3.left = node1
node3.right = node4
node1.right = node2
solution = Solution()
result = solution.kthSmallest(node3, k=1)
print(result)
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
// 解题关键:中序遍历
// https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/description/
// 给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数kthSmallest来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
// 只要利用二分搜索树的中序遍历,就可以完成。
public class Solution {
private int count = 0;
private int res = 0;
private void dfs(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
// 什么都不做
return;
}
dfs(node.left);
count--;
if (count == 0) {
this.res = node.val;
}
dfs(node.right);
}
// k 如果在方法传递的过程中是值传递,所以把它设置为成员变量,这样就是引用传递
// 因为我们要用到 k 全局的值,去数出,我是第几个中序遍历到的值
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
count = k;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeNode treeNode1 = new TreeNode(10);
TreeNode treeNode2 = new TreeNode(15);
TreeNode treeNode3 = new TreeNode(20);
treeNode2.left = treeNode1;
treeNode2.right = treeNode3;
Solution solution = new Solution();
int kthSmallest = solution.kthSmallest(treeNode2, 2);
System.out.println(kthSmallest);
}
}
下面是 Python 的另一种写法:使用 global 关键字,仍需使用辅助函数:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
global counter, res
counter = 0
res = 0
def dfs(root, k):
if not root:
# 如果是空,直接退出
return
dfs(root.left, k)
global counter, res
counter += 1
if counter == k:
res = root.val
dfs(root.right, k)
dfs(root, k)
return res
参考代码 2:模拟系统栈的方式:使用二叉树非递归遍历的通用方法。使用同样的的方法还可以解决 「力扣」LeetCode 第 144 题:二叉树的前序遍历 (opens new window)、「力扣」第 94 题:二叉树的中序遍历 (opens new window)、「力扣」第 145 题:二叉树的后序遍历 (opens new window)。
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
# 模拟系统栈的方式实现,是一种比较通用的做法,
# 可以作为二叉树的三种非递归遍历
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
# 0 表示当前遍历到它,1 表示压入栈
# 刚开始是 1 ,不要写成 0 了
stack = [(1, root)]
while stack:
command, node = stack.pop()
if node is None:
# 不能写 return ,这不是递归
continue
if command == 0:
k -= 1
if k == 0:
return node.val
else:
# 此时 command == 1 的时候,表示递归遍历到的
# 注意:写的时候倒过来写
stack.append((1, node.right))
stack.append((0, node))
stack.append((1, node.left))
其实入栈的时候,就可以判断,我们只将非空结点入栈,推荐下面这种写法:
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
stack = [(1, root)]
while stack:
command, node = stack.pop()
if command == 0:
k -= 1
if k == 0:
return node.val
else:
# 模拟系统栈实现中序遍历(先左边、再自己、再右边)
# 注意:写的时候倒过来写
if node.right:
stack.append((1, node.right))
stack.append((0, node))
if node.left:
stack.append((1, node.left))
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution4 {
private enum Action {
// GO 表示递归处理
// ADDTORESULT 表示当前马上执行将结点的值添加到结果集中
GO, ADDTORESULT
}
private class Command {
private Action action;
private TreeNode node;
public Command(Action action, TreeNode node) {
this.action = action;
this.node = node;
}
}
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
Stack<Command> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.add(new Command(Action.GO, root));
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Command cur = stack.pop();
TreeNode node = cur.node;
if (cur.action == Action.ADDTORESULT) {
k--;
if (k == 0) {
return node.val;
}
} else {
assert cur.action == Action.GO;
if (node.right != null) {
stack.add(new Command(Action.GO, node.right));
}
stack.add(new Command(Action.ADDTORESULT, node));
if (node.left != null) {
stack.add(new Command(Action.GO, node.left));
}
}
}
throw new RuntimeException("参数错误");
}
}
# 方法一:先得到中序遍历的结果,然后找到第 k 大元素
我们利用了二分搜索树的有序性,二分搜索树的中序遍历得到的是一个有序数组,直接得到结论。
Java 代码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(root, res);
return res.get(k - 1);
}
private void dfs(TreeNode node, List<Integer> res) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
dfs(node.left, res);
res.add(node.val);
dfs(node.right, res);
}
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
,遍历了整个树。 - 空间复杂度:
,用了一个数组存储中序序列。
# 方法二:在递归的时候不记录全部结果,只记录计数器
Java 代码:
public class Solution {
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
count = k;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
private int count = 0;
private int res = 0;
private void dfs(TreeNode node) {
// 先写递归终止条件
if (node == null) {
// 什么都不做
return;
}
dfs(node.left);
count--;
if (count == 0) {
this.res = node.val;
}
dfs(node.right);
}
}
分析:因为二分搜索树具有顺序性,所以我们可以用类似快速排序的 partition 操作来完成
1、二分搜索树的有序性;2、二叉树中序遍历,特别地,
简而言之就是在中序遍历的时候数个数,第 1 个遍历到的是第 1 个最小的元素,第 2 个遍历到的是第 2 个最小的元素,数到第 k 个够数了,就不用再遍历了。
Python 代码:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# 230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
# 给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
class Solution:
# 使用中序遍历得到 BST 第 k 小的那个元素
def __init__(self):
self.k = None
self.res = None
def __dfs(self, node):
if node is None:
return
self.__dfs(node.left)
self.k -= 1
if self.k == 0:
self.res = node.val
return
self.__dfs(node.right)
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
self.k = k
self.__dfs(root)
return self.res
等价写法:
Python 代码:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.counter = 0
self.res = 0
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
# 使用递归的方法,中序遍历
if root.left:
# 不是空,才继续遍历
self.kthSmallest(root.left, k)
self.counter += 1
# print(root.val)
if self.counter == k:
# 注意:千万不能在这里返回,后序遍历还要继续进行下去
self.res = root.val
return
if root.right:
self.kthSmallest(root.right, k)
return self.res
Python 代码:推荐写法
# Definition for a binary tree node.
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# 这种写法比 3 更好一些,在入栈的时候,就判断结点是不是空,非空才入栈
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
stack = [(1, root)]
while stack:
command, node = stack.pop()
if command == 0:
k -= 1
if k == 0:
return node.val
else:
# 模拟系统栈实现中序遍历(先左边、再自己、再右边)
if node.right:
stack.append((1, node.right))
stack.append((0, node))
if node.left:
stack.append((1, node.left))
Python 代码:
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root, k):
stack = [(1, root)]
while stack:
command, node = stack.pop()
if command == 0:
k -= 1
if k == 0:
return node.val
else:
# 模拟系统栈实现中序遍历(先左边、再自己、再右边)
if node.right:
stack.append((1, node.right))
stack.append((0, node))
if node.left:
stack.append((1, node.left))
作者:liweiwei1419 链接:https://suanfa8.com/binary-search-tree/solutions/0230-kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst 来源:算法吧 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。