# 「力扣」第 130 题:被围绕的区域
# 题目描述
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 board ,由若干字符 'X' 和 'O' ,找到所有被 'X' 围绕的区域,并将这些区域里所有的 'O' 用 'X' 填充。
示例 1:
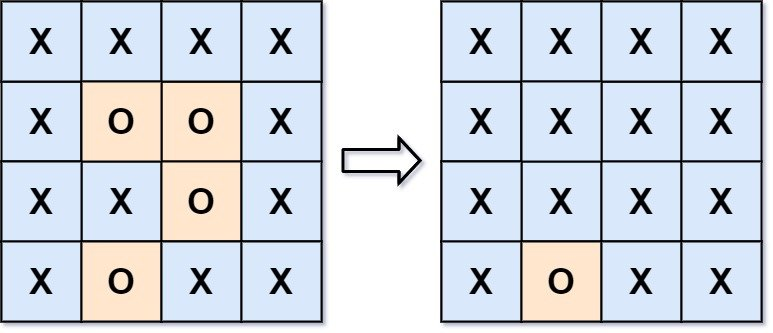
输入:board = [["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","O","X"],["X","X","O","X"],["X","O","X","X"]]
输出:[["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","X","X","X"],["X","O","X","X"]]
解释:被围绕的区间不会存在于边界上,换句话说,任何边界上的 'O' 都不会被填充为 'X'。 任何不在边界上,或不与边界上的 'O' 相连的 'O' 最终都会被填充为 'X'。如果两个元素在水平或垂直方向相邻,则称它们是“相连”的。
示例 2:
输入:board = [["X"]]
输出:[["X"]]
提示:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 200board[i][j]为'X'或'O'
# 思路分析
根据题意: 四个边的 O 以及与其相邻的 O 都无法被 X 包围 ,因此,可以先把四周的 O 以及 O 的连通分量全部变成 '-'(一个与 O 和 X 不同的字符即可)。然后再遍历一次棋盘,把 - 恢复成 O。
可以使用深度优先遍历与广度优先遍历。
# 方法一:深度优先遍历
关键:与边界相连 O 不能被替换成 X。
具体步骤:
- 第 1 步:把四周有
O的地方都替换成为-,在四周进行floodfill算法(染色); - 第 2 步:再从头到尾遍历一遍,把
O换成X,把-换成O。
具体请见 参考代码 1 和 参考代码 2:
参考代码 1:
public class Solution {
public void solve(char[][] board) {
// 特殊判断
int rows = board.length;
if (rows == 0) {
return;
}
int cols = board[0].length;
if (cols == 0) {
return;
}
int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}};
// 第 1 步:把四周的 `0` 以及与 `0` 连通的 `0` 都设置成 `-`
// 第 1 列和最后 1 列
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
if (board[i][0] == 'O') {
dfs(i, 0, rows, cols, board, directions);
}
if (board[i][cols - 1] == 'O') {
dfs(i, cols - 1, rows, cols, board, directions);
}
}
// 第 1 行和最后 1 行
for (int j = 1; j < cols - 1; j++) {
if (board[0][j] == 'O') {
dfs(0, j, rows, cols, board, directions);
}
if (board[rows - 1][j] == 'O') {
dfs(rows - 1, j, rows, cols, board, directions);
}
}
// 第 2 步:遍历一次棋盘,
// 1. 剩下的 0 就是被 X 包围的 0,
// 2. - 是原来不能被包围的 0,恢复成 0
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
} else if (board[i][j] == '-') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
}
// 已经是 X 的地方不用管
}
}
}
private boolean inArea(int x, int y, int rows, int cols) {
return x >= 0 && x < rows && y >= 0 && y < cols;
}
private void dfs(int i, int j, int rows, int cols, char[][] board, int[][] directions) {
if (inArea(i, j, rows, cols) && board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = '-';
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int newX = i + directions[k][0];
int newY = j + directions[k][1];
dfs(newX, newY, rows, cols, board, directions);
}
}
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:
,其中 rows和cols分别为矩阵的行数和列数,深度优先遍历过程中,每一个单元格至多只会被标记一次; - 空间复杂度:
,深度优先遍历最多使用的栈的开销为整个棋盘的大小。
# 方法二:广度优先遍历
参考代码 2:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Solution {
public void solve(char[][] board) {
int rows = board.length;
if (rows == 0) {
return;
}
int cols = board[0].length;
int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}};
// 第 1 步:把四周的 'O' 全部推入队列,通过广度优先遍历,把与 'O' 连通的地方全部编辑
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
if (board[i][0] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, 0});
}
if (board[i][cols - 1] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, cols - 1});
}
}
for (int j = 1; j < cols - 1; j++) {
if (board[0][j] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{0, j});
}
if (board[rows - 1][j] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{rows - 1, j});
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] top = queue.poll();
int i = top[0];
int j = top[1];
board[i][j] = '-';
for (int[] direction : directions) {
int newX = i + direction[0];
int newY = j + direction[1];
if (inArea(newX, newY, rows, cols) && board[newX][newY] == 'O') {
queue.offer(new int[]{newX, newY});
}
}
}
// 第 2 步:恢复
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '-') {
board[i][j] = 'O';
} else if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
private boolean inArea(int x, int y, int rows, int cols) {
return x >= 0 && x < rows && y >= 0 && y < cols;
}
}
复杂度分析:(同参考代码 1)
# 方法三:并查集
- 把四周的
O都和一个虚拟结点合并起来; - 在内部,只看两个方向,把
O都合并起来; - 最后再扫一次数组,不和「虚拟结点」连接的
O都标记成X。
并查集的写法容易受 floorfill 的影响,用并查集的时候,其实 只用每一行的右边和下面都看一下,只针对 O,能合并就合并一下。
参考代码 3:
public class Solution {
public void solve(char[][] board) {
int rows = board.length;
if (rows == 0) {
return;
}
int cols = board[0].length;
if (cols == 0) {
return;
}
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(rows * cols + 1);
int dummyNode = rows * cols;
// 填写第 1 行和最后一行
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (board[0][j] == 'O') {
unionFind.union(getIndex(0, j, cols), dummyNode);
}
if (board[rows - 1][j] == 'O') {
unionFind.union(getIndex(rows - 1, j, cols), dummyNode);
}
}
// 填写第 1 列和最后一列
for (int i = 1; i < rows - 1; i++) {
if (board[i][0] == 'O') {
unionFind.union(getIndex(i, 0, cols), dummyNode);
}
if (board[i][cols - 1] == 'O') {
unionFind.union(getIndex(i, cols - 1, cols), dummyNode);
}
}
int[][] directions = new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 0}};
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
for (int[] direction : directions) {
int newX = i + direction[0];
int newY = j + direction[1];
if (newX < rows && newY < cols && board[newX][newY] == 'O') {
unionFind.union(getIndex(i, j, cols), getIndex(newX, newY, cols));
}
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < rows - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols - 1; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'O') {
if (!unionFind.isConnected(getIndex(i, j, cols), dummyNode)) {
board[i][j] = 'X';
}
}
}
}
}
private int getIndex(int x, int y, int cols) {
return x * cols + y;
}
class UnionFind {
private int[] parent;
public UnionFind(int n) {
this.parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public boolean isConnected(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
public int find(int x) {
while (x != parent[x]) {
parent[x] = parent[parent[x]];
x = parent[x];
}
return x;
}
public void union(int x, int y) {
int xRoot = find(x);
int yRoot = find(y);
if (xRoot == yRoot) {
return;
}
parent[xRoot] = yRoot;
}
}
}
复杂度分析:可以见「力扣」第 200 题:岛屿数量 官方题解 (opens new window) 的复杂度分析。
作者:liweiwei1419 链接:https://suanfa8.com/backtracking/solutions-3/0130-surrounded-regions 来源:算法吧 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。